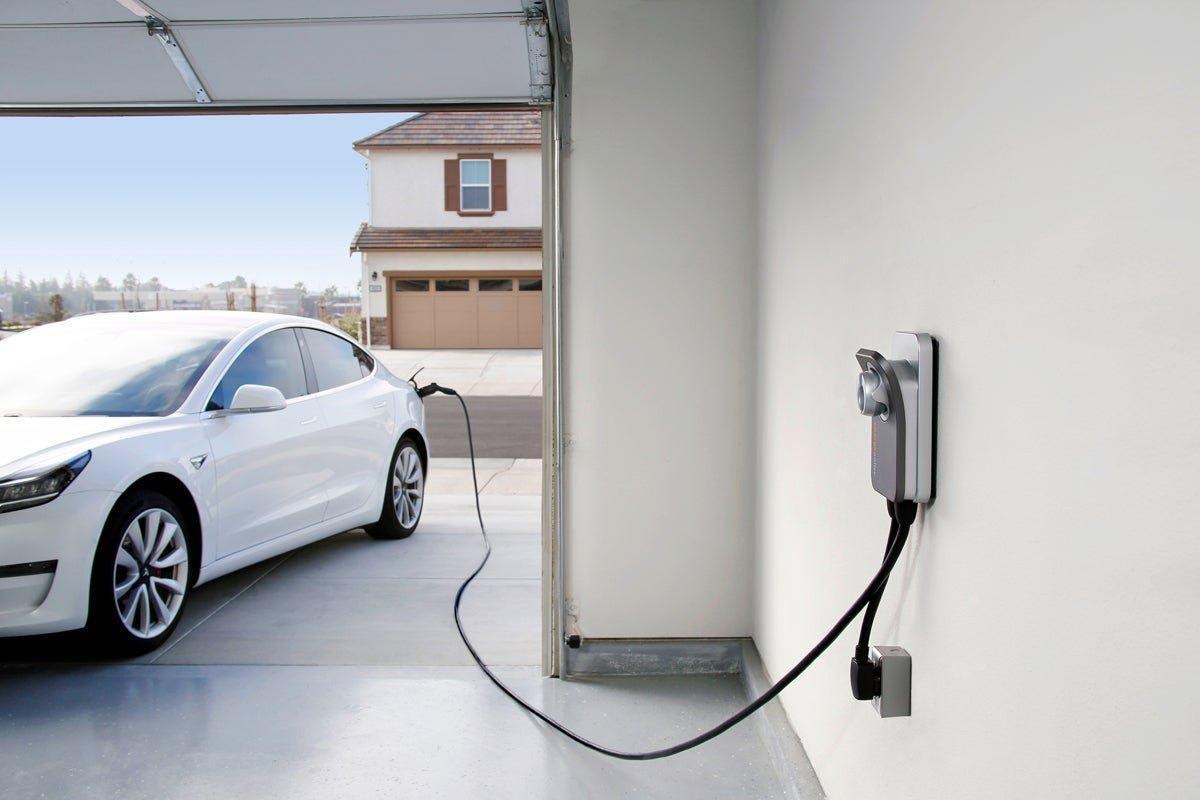
An electric car runs on electricity rather than gasoline. Quiet, fast, and completely environmentally friendly, the future is confidently becoming the present. On average, it takes about 7-8 hours to charge an electric car from the regular power grids.
However, from turbo-charging stations, it will be set in 2.5-3 hours. It is not only the charger power that is important but also the battery’s capabilities and the electric vehicle’s onboard charger (both DC and AC).
What kind of batteries do electric cars use?
The electric motor in an electric car must always be powered at the highest level. This has a direct impact on how long electric cars batteries last. That is why improvements are continuously being sought in battery technology.
Electric cars are vehicles that are driven using electric energy stored in a battery. This technology makes the electric car twice as cheap to operate compared to a gasoline-powered car and more manoeuvrable on the road. There are already several batteries for electric cars: lithium-ion, lithium-sulfur, aluminium-ion, and metal-air.
Lithium-ion batteries are mostly used in electric cars. Batteries of any type are dialled up in cells connected in parallel and in series to form massive assemblies of the required capacity. A new battery is designed for an extended period of use, and its full charge is sufficient for maximum mileage – but over time, the car battery wears out and needs to be replaced. And if some of the cells are damaged, the modular design of the battery allows it to be repaired.
Find car finance deals with the best rates!
My monthly budget is
Calculating charging time
How can one know if it takes long to charge an EV? The maximum charging rate may not be uniform, and the time may vary, but in general, the electric vehicle charging time is calculated by the formula:
Battery capacity (kWh) / Charger capacity (kW) = Charging time (h).
Factors that impact charging time
It all depends on the built-in charger of the electric car itself, the battery’s condition, the temperature, and its residual capacity. And most importantly, what kind of power supply is used: whether it is connected to the household power grid, a special home charging unit, a fast charger, or a super-fast charger. Let’s take a look at several factors impacting charging time.
Types of charging stations
To begin with, let’s look at the types of charging stations for electric cars: ultrafast, fast, and slow. These charging stations differ in capacity and, therefore, in charging speed. Each type of charging station has its own charging infrastructure, which in turn is divided by working capacity and working current (AC or DC).
Ultrafast charging stations are by far the fastest way to charge an electric car. They can be found on highways or in large public parking lots. These stations provide high-power DC or AC and charge a vehicle up to 80% in 20-40 minutes. In most cases, ultra-fast stations shut down when the electric car’s kWh battery is about 80% charged to protect the battery and extend its life.
Fast charging stations charge the electric vehicle with single- or three-phase alternating current and output 7 kW or 22 kW (single- or three-phase) at 32 amps. The charging time at such stations is individual and depends on the capacity of the battery charger of an electric car. Still, approximately, a 7 kW charger station recharges a compatible electric vehicle with a 30 kW⋅h battery in 3-5 hours. A 22 kW charger charges a compatible electric car in 1-2 hours.
Slow stations are designed for up to 3 kW, and there are some models capable of delivering 6 kW. Since slow charging stations offer alternating current just like the fast ones, the time it takes to charge an electric vehicle varies depending on the onboard charger’s capacity. To give you an example: a full charge of a 3kW charging unit typically takes 6-12 hours. Slow charging stations can be stationary or portable.
Battery size
Almost every electric vehicle uses a different type of battery. Batteries differ in capacity and provide different driving ranges. Although the maximum distance an electric car can travel also depends on its design and weight, one can use this figure to compare batteries. On average, there are cars on the market with a battery capacity of 60.7 kilowatt-hours.
Battery state (Empty vs. Full)
The condition of the battery also affects battery life and charge time. It’s recommended to keep the charge level between 20 and 80% (i.e., do not charge above 80% and do not allow the charge to drop below 20%).
Charging rate of the battery
The battery capacity of any electric vehicle is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The batteries of modern electric cars consist of many connected batteries. To make the battery larger, you can either combine more cells into it or make the batteries themselves larger.
For example, the Tesla Model X Long Range has a corresponding index of 100 kWh. That is, its battery can deliver 100 kW of power for one hour or 1 kW for a hundred hours.
Environmental factors
Factors like the temperature outside may affect the battery as well. The disadvantage is the small temperature range of lithium-ion batteries (from -20 to +50°C). When used outside of these values, the battery performance deteriorates – in the cold, the capacity decreases, and the battery may be unstable in the heat.
Types of charges
Not only do electric cars have different types of batteries, but there are also different charging cables. There are three types in total. Below we will look at each of them in detail.
Type 1 – Rapid Charging
The first type is the new generation of charging points in the U.K., ultra-fast chargers. Their specifications are 100+ kW and up to 350 kW. Such a charger provides almost a full charge (up to 80%) in just 30-50 minutes. Of course, this time can be affected by the type of battery you have and the charger.
Type 2 – Fast Charging
The next type is fast charging. It can output 7-22 kW and fully charge the car in 3-4 hours. It is one of the most popular types of charging in the UK today. There are currently over 42,000 charging jacks in over 15,500 locations.
Type 3 – Slow Charging
Finally, the last type of charger is the slow charger. Their maximum power is only 3.6 kW. Such chargers are usually installed in the homes of electric car owners, as it takes 6-12 hours to fully charge with such a device – ideal to leave overnight.
How much range do you get per hour of charging?
Now let’s take a look at the miles of range added per hour of charging. For it to be convenient, we’ve created a table with all the data.
| Miles of range added per hour of charging | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.7kW slow | 7kW fast | 22kW fast | 43-50kW rapid | 150kW rapid |
| Up to 15 miles | Up to 30 miles | Up to 90 miles | Up to 90 miles in 30 mins | Up to 200 miles in 30 mins |
So, what conclusions can be drawn from this table? It all depends on the capacity of your battery and its efficiency. Therefore, a small car with a full battery would be ideal. They can provide up to 30 miles of range per hour on a 7kW charge.
Heavier cars and hybrids provide ~20 miles of range per hour at 7 kW. Important – hybrids are less efficient than standard electric cars. It’s also worth keeping in mind that your electric vehicle can be very much affected by the environment. So, it will charge better and have a better range in the summer than in the winter.
How far can an electric car go?
How far can you drive with a fully charged battery? This is, perhaps, the first and most important question in any discussion of electric cars. We decided not just to answer it with numbers but to make a rating of the most capable representatives of battery-powered vehicles.
The actual range of an electric car may differ from the manufacturer’s stated range by five or even 150 km. This applies to all models: even electric vehicles with an extensive range have similar figures.
- Tesla Roadster (2018) – 998 km
- Jaguar i-Pace – 480 km
- Renault ZOE – 400 km
- Hyundai Kona EV – 385 km
- Chevrolet Bolt EV – 383 km
- Volkswagen e-Golf – 300 km
- Nissan Leaf II – 243 km
- Smart ForTwo Electric Drive – 160 km
Where can I charge my EV?
You can charge the electric car from a standard European socket with a nominal voltage of 220 volts. Nevertheless, a dedicated electric car charging station has speed and safety advantages. Here are two of the most common ways to charge your car.
Public charging
Plugging in at home is the easiest way to charge your electric car for each day fully. But with more and more public charging stations on the road – in locations ranging from remote workshops to highways – the recharging process is easier than ever.
Fully electric vehicles are compatible with two types of public charging stations. AC charging points are usually located in places like shopping malls, gyms, and parking lots. DC quick-charge points are most often located on highways and public roads.
Although some charging points are free, most require payment through several convenient methods, including mobile apps, an account, or a contactless bank card. The cost of charging in public places is usually made up of an initial connection, charging time (cost per hour), and/or the amount of energy used (cost per kWh).
Home charging
Spending a mere five minutes at the charging station is out of the question: at least 20-30 minutes are needed for an incomplete charge, and a full charge will take several hours. This is also why owners prefer to plug their cars in at night while they sleep at home.
How much will it cost to charge my car at home?
Of course, each case is worth considering individually and calculating based on your own car and your tariff. However, let’s look at an abstract example. So, let’s say you drive about 1,000 miles a month. If you charge your car at home using the Economy 7 tariff, your EV recharging bill at home would be £37 to £63 per month. So your annual total will be somewhere between £450 and £750.
What is top-up charging?
You probably don’t wait until your phone runs out of power to put it on the charger, do you? You can do the same with your car. For example, you can connect to a charging station at a gas station or supermarket. That’s top-up charging.
What are popular electric car charging times?
| Brand | Car model | Battery capacity | Total electrical range | Charging capacity | Range after charging 1 hour at a wallbox | Charging time at a wallbox¹ | Charging time at a domestic socket¹² | Plug Type | Energy consumption [kWh/100km] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audi | Q7 e-tron quattro | 17.3 kWh | 56 km | 7.2 kW | 35 km | 2.5 h | 8 h | Type 2 | 19 kWh |
| BMW | X5 xDrive40e | 9.2 kW | 31 km | 3.7 kW | 25 km | 2.5 h | 3.5 h | Type 2 | 15.3 kWh |
| Chevrolet | Volt | 10.3 kWh | 85 km | 4.6 kW | 20 km | 2.5 h | 5h | Type 2 | 22.4 kWh |
| Jaguar | I-PACE | 90 kWh | 480 km | 7.2 | 50 kW | 30 | 270 km | 13 | 2 h | 39.5 h | Type 2 | 21.2 kWh |
Charging tips
Here are some useful tips that may help you with charging your EV.
- Manage your charging time wisely. Plan your charging time so that your electric car’s battery is fully charged before you leave the road. This will allow you to gain a couple of kilometres if the electric car has been idle for a long time without recharging from the power grids. This arrangement of charging times will not only increase your range but will also help you save on fare differences if you use overnight fares to recharge your electric car, for example.
- Plan your route. Try to drive on pre-planned roads that require less energy. Avoid areas with fast traffic, if possible. At the same time, traffic jams are no problem for an electric car – they don’t use much energy.
- Be guided by your own electric car’s capabilities. Only you know how many kilometres your electric car will travel on one charge. Even the manufacturer cannot give an exact figure for the range of any electric car brand, as it depends not only on the technical characteristics but also on the driving style and weather conditions.
- Have a backup plan for recharging your electric vehicle. Sometimes, when you drive up to a charging station, you’ll find it being repaired or taken out of service. To not be held hostage by this situation, we recommend taking a mobile charging station on the road. With it, you will be able to charge your electric car from any outlet. Additionally, we recommend buying an extension cord for charging. It will be helpful both for everyday use and for travel.
- Be aware of weather conditions. Rain, heat, and cold affect your electric vehicle’s battery consumption. In winter, the range is significantly reduced, and you will need to recharge more. When making travel arrangements, be sure to take this factor into account.
Table of Contents